


A vocabulary that can feel like a moving target has been introduced by the quick development of generative AI. For business leaders and developers looking to develop AI solutions, two terms dominate the conversation: "Foundation Models" and "Large Language Models" (LLMs). While often used interchangeably in casual tech circles, the distinction between them is the difference between a Swiss Army knife and a high-end chef’s knife. One is defined by its versatile multi-tool nature; the other by its specialized, world-class precision in a single domain.
Choosing the wrong architecture for your generative AI integration can lead to "technical debt" or inefficient resource allocation. Whether you are building a multimodal diagnostic tool or a specialized legal chatbot, understanding the foundation model vs LLM dynamic is the first step toward a scalable AI strategy.
To understand the foundations of large language models, we must first look at the hierarchy of AI. In the simplest terms, a foundation model is a broad category of AI models trained on vast, diverse datasets so they can be adapted to a wide range of downstream tasks.
Large language models are a subset of foundation models. In particular, these are foundation models with excellent Natural Language Processing (NLP) skills that have been trained mostly on text.
The term foundation model was popularized by the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered AI (HAI). These models represent a shift from "task-specific AI" (where you build one model to predict churn and another to recognize cats) to "general-purpose AI."
A true foundation LLM or multimodal model possesses three core traits:
While LLMs dominate the headlines, vision foundation models are transforming industries like manufacturing and healthcare. Models like Segment Anything (SAM) or DALL-E are examples where the "foundation" is visual data rather than text. When you combine these, you get multimodal models AI that can "see" a medical X-ray and "write" a report simultaneously.
If foundation models are the bedrock, LLM foundation models are the skyscrapers built specifically for communication. An AI large language model focuses on the intricacies of human syntax, grammar, and context.
For companies focused on developing AI chatbots or internal knowledge bases, a specialized llm foundation model is the most cost-effective path. These models are optimized for:
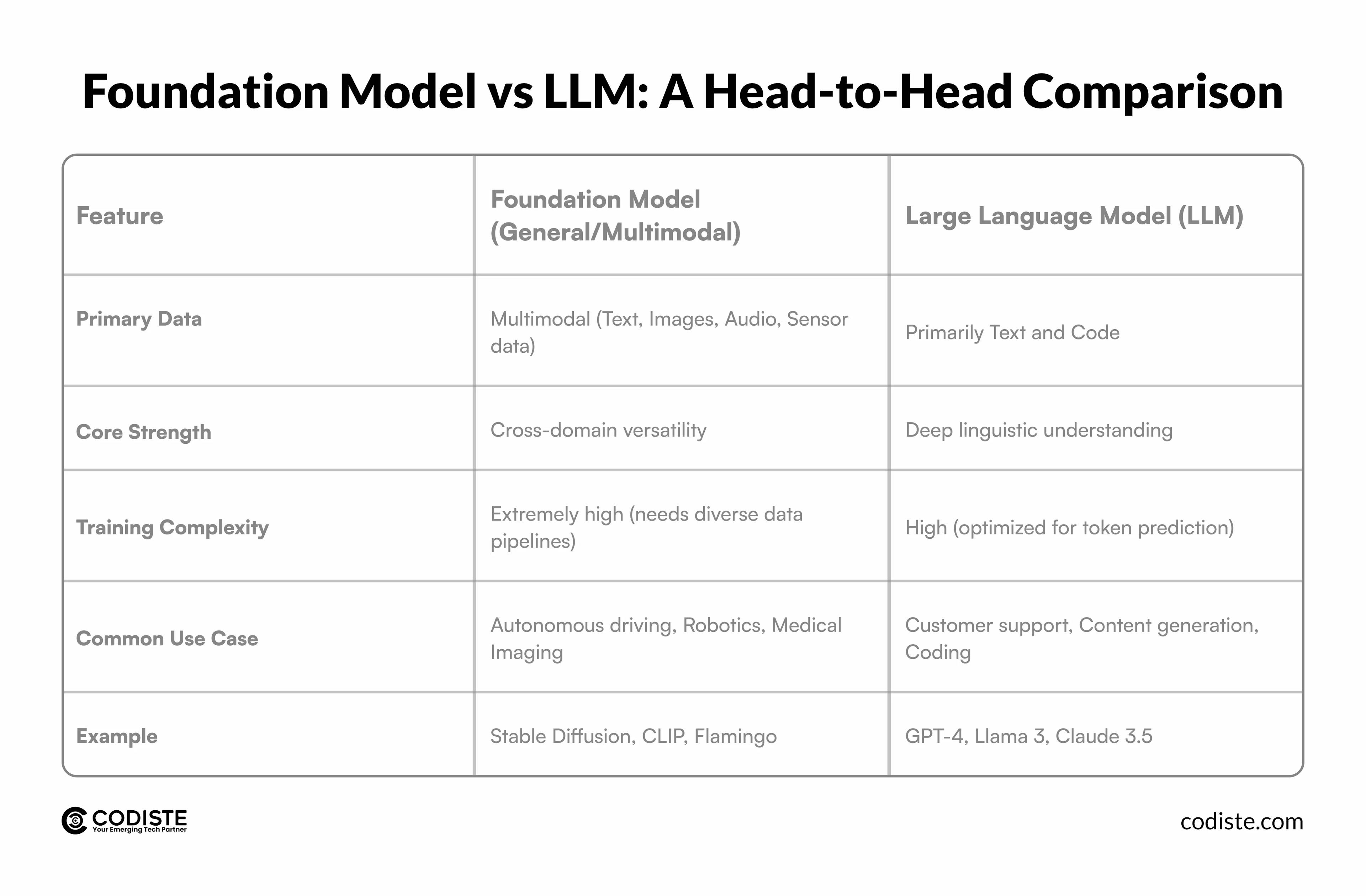
When deciding between a general foundation model vs LLM, it helps to look at the specific technical and operational trade-offs.
In the middle of this debate sits the concept of hugging face embeddings. Embeddings are the mathematical representations of data. Whether you use a foundational model vs LLM, you will likely use embeddings to help the model "understand" the relationship between different data points. This is crucial for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which allows your AI to access private company data without retraining the entire model.
The foundations of LLMs and other foundation models rely almost exclusively on the Transformer architecture. This architecture uses a "self-attention" mechanism, allowing the model to weigh the importance of different parts of the input data.
One of the most significant foundational models vs traditional models differences is the training method. Traditional models required humans to label every piece of data. Foundation models use self-supervised learning, where the model essentially "hides" part of the data from itself and tries to predict it (e.g., predicting the next word in a sentence or the missing patch in an image).
As we look at vision founation models, the architecture evolves to handle "tokens" that aren't just words. In a multimodal foundation model vs LLM example, an image is broken down into small patches (visual tokens) and processed alongside text tokens. This makes it possible for many kinds of information to interact seamlessly.
Ready to transform your business with custom AI?
For an executive looking at AI development services, the choice isn't just about "which model is smarter." Its about which model delivers the best ROI.
Training a foundation LLM from scratch is a multi-million-dollar endeavor reserved for the "Big Tech" giants. Most businesses should focus on fine-tuning or prompt engineering of existing models.
If your product roadmap includes moving from text-based support to video-based interaction, starting with a multimodal foundation model might be the better long-term play. However, for 90% of business automation needs, llm vs fm ends with the LLM winning on speed-to-market.
The debate of foundation model vs LLM isn't about finding a "winner." Finding the ideal instrument for your unique architectural requirements is the key. While more comprehensive foundation models offer the multimodal flexibility needed for the next generation of industrial AI, LLMs offer unmatched depth in human communication.
However, the complexity of generative AI integration, from managing hugging face embeddings to optimizing token costs, requires more than just a model choice. It requires a partner who understands the full stack of AI development.
At Codiste, we specialize in turning these complex neural networks into tangible business value. Whether you are looking to develop AI solutions that automate your workflow or need expert AI development services to build a custom multimodal platform, our team ensures your AI strategy is both cutting-edge and cost-effective. Don't just follow the AI trend, build your future on a foundation that lasts.




Every great partnership begins with a conversation. Whether you’re exploring possibilities or ready to scale, our team of specialists will help you navigate the journey.